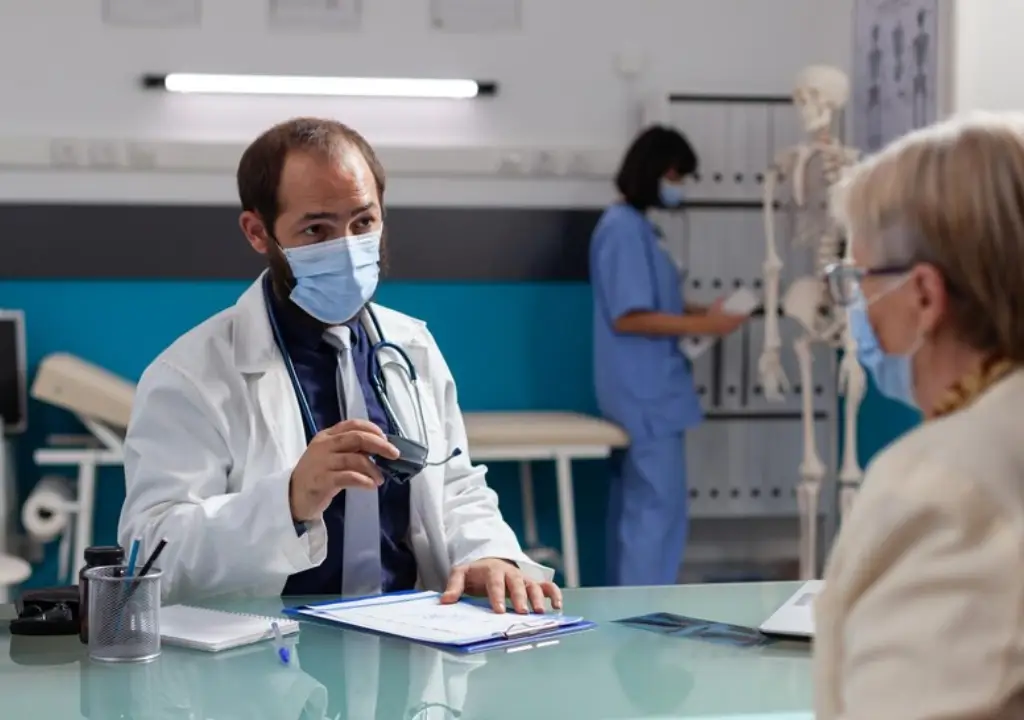
Introduction to General Health Panel Blood Test
A general health panel blood test is a comprehensive diagnostic tool that evaluates your overall health through various blood tests. This test checks multiple aspects of your body’s functions, such as liver, kidney, heart health, and blood sugar levels. Regular health screenings are critical as they help detect potential health issues early, allowing for timely interventions and better health management.
Understanding what happens during a general health panel blood test can help you feel more comfortable and prepared. From the initial blood draw to the detailed analysis of the samples, each step plays a vital role in ensuring accurate and reliable results.
Understanding the Blood Test Procedure
The blood test procedure is straightforward but involves several precise steps to ensure the accuracy of your results. A phlebotomist, a trained professional responsible for drawing blood, plays a key role in this process. The procedure involves collecting a blood sample, which is then processed and analyzed in a laboratory. These tests provide valuable information about your body’s internal state, making them essential for routine checkups and diagnosing specific conditions.
Phlebotomists are trained to make the blood draw process as quick and painless as possible. They follow strict hygiene and safety protocols to minimize any risk of infection. The entire procedure, from blood collection to lab analysis, ensures that the test results accurately reflect your health.
Preparing for the Blood Test
Preparation is crucial for obtaining accurate blood test results. Before the test, your healthcare provider may give specific instructions, such as fasting for 8–12 hours or avoiding certain medications. Proper preparation ensures that the blood sample collected is free of interference from food, drinks, or substances that could skew the results.
Patients are often advised to stay hydrated, avoid alcohol, and follow any other guidelines provided. By adhering to these instructions, you can help ensure that your test results are reliable, which is key to making informed decisions about your health.
Step 1: Patient Identification and Preparation
The first step in the testing process is patient identification, which is crucial for preventing errors. Proper identification ensures that the right test results are matched with the correct patient. You will typically be asked to confirm your name, date of birth, and other personal details, which will be verified against your identification tags.
Once identification is confirmed, the phlebotomist will prepare the blood draw site by cleaning it with an alcohol swab. This step is important to maintain sterility and prevent potential infection. The phlebotomist will also ensure that you are comfortable and ready for the procedure, which helps reduce any anxiety about the blood draw.
Step 2: Phlebotomy Procedure – Blood Draw Steps
Phlebotomy involves drawing blood from a vein, usually in your arm. A tourniquet is placed around your upper arm to make your veins more prominent. The phlebotomist will then draw the blood with a sterile needle attached to a Vacutainer or syringe. Blood collection tubes of different colors are used, each indicating a specific type of test to be conducted.
Different tubes are used for different purposes; for example, some are for clotting studies, while others may be used for chemistry panels. After drawing the required amount of blood, the needle is removed, and pressure is applied to the puncture site to stop any bleeding. This step is conducted carefully to ensure minimal discomfort and to maintain sample integrity.
Step 3: Blood Sample Handling and Labeling
After the blood is drawn, each sample is immediately labeled with your information using barcode scanning to prevent mix-ups. Proper labeling is critical to ensure the sample is correctly identified throughout the testing process. The labeled samples are then handled with care to maintain the quality and integrity of the specimen.
Handling includes storing the blood samples in specific conditions depending on the tests to be performed. Quality control measures are also part of this stage, such as checking the tubes for proper filling and ensuring the samples are not hemolyzed (damaged). These precautions help ensure that the blood samples remain viable for accurate analysis.
Step 4: Blood Sample Analysis in the Lab
Once the samples reach the lab, they undergo a series of analyses conducted by laboratory technicians and automated analyzers. A centrifuge is often used to separate blood components like serum and plasma, essential for various tests. Each test, from basic blood counts to complex biochemical assays, is performed using state-of-the-art technology and standardized procedures.
Laboratory technicians perform the tests using automated hematology analyzers, biochemical assay equipment, and other advanced tools. These machines are calibrated regularly with quality control samples to ensure accuracy. Using automated analyzers reduces the chances of human error and provides precise and reliable results.
Common Tests in a General Health Blood Panel
Common tests in a General Health Panel provide a broad overview of your overall health. They are designed to check the status of major organs, blood components, and other key health indicators, helping identify any abnormalities that may need further investigation or management. Understanding the importance of regular tests for preventative care ensures that potential health issues are detected early, allowing for timely intervention and more effective health management.
Lipid Panel
This test measures cholesterol and triglycerides to assess heart health. It helps determine your risk of cardiovascular diseases by evaluating good (HDL) and bad (LDL) cholesterol levels.
Liver Function Tests (LFTs)
LFTs evaluate liver health by measuring enzymes, proteins, and other substances in your blood. Abnormal levels can indicate liver damage or disease, such as hepatitis or fatty liver.
Kidney Function Tests
These tests check how well your kidneys are working by measuring levels of waste products like creatinine and urea. They help identify kidney conditions and monitor the effectiveness of treatments.
Coagulation Tests
Coagulation tests assess the blood’s ability to clot, which is important for diagnosing bleeding disorders. They help determine whether blood clotting factors are within a normal range.
Hormone Tests
Hormone tests evaluate the levels of various hormones in your blood to check for endocrine disorders, such as thyroid imbalances or reproductive health issues.
Laboratory Analysis and Error Checks
Automated hematology analyzers and other diagnostic equipment perform tests on the samples during the analysis. The lab employs stringent error checks to ensure that the results are accurate. Calibration standards are used to validate the analyzers, and error check systems detect any anomalies in the test results, prompting further investigation if needed.
Quality control samples are run alongside patient samples to ensure the analyzers function correctly. These steps are crucial to maintaining the reliability of the test results, ensuring that the data provided to your healthcare provider is accurate and actionable.
Step 5: Reporting Test Results
Once the analysis is complete, the results are compiled and interpreted. Test results are compared against reference ranges, which indicate the normal values for each test. The Laboratory Information System (LIS) manages the results, ensuring they are accurately reported and easily accessible.
Patients can access their results through a secure patient portal to review and discuss the findings with their healthcare provider. Understanding the results is crucial, as it helps patients make informed decisions about their health and any necessary follow-up actions.
Blood Sample Transportation and Storage Protocols
Proper transportation and storage of blood samples are essential to maintaining their integrity. Samples are transported from collection sites to the laboratory using specialized courier services that follow strict protocols. This ensures the samples are kept at the correct temperature and handled carefully throughout the journey.
In the laboratory, samples are stored under specific conditions, depending on the test type to perform. Proper sample storage ensures the stability of the analytes, which is crucial for obtaining accurate test results. Adherence to these protocols will ensure the quality of the results is maintained.
Special Tests and Panels in General Health Testing
Special tests in a General Health Panel provide additional insights into specific health conditions. These tests assess various functions and help diagnose issues that standard panels might not fully capture, offering a more detailed evaluation of the patient’s health.
Blood Gas Analyzer
It measures the levels of oxygen, carbon dioxide, and pH in the blood. It is often used in critical care settings. This test helps assess lung function and acid-base balance in the body.
Serology Testing
Detects antibodies in the blood, which can indicate infections or immune responses. Serology tests commonly diagnose conditions like viral infections and autoimmune diseases.
Electrolyte Panel
Assesses the balance of electrolytes such as sodium, potassium, and chloride, vital for various body functions. Imbalances can indicate dehydration, kidney issues, or other health problems.
Immunoassay
Measures specific proteins or hormones in the blood, helping diagnose various conditions, including hormone imbalances, allergies, and infectious diseases.
Quality Control and Validation in Lab Testing
Quality control is a cornerstone of laboratory testing, ensuring reliable and accurate results. The use of quality control samples helps validate the testing process, confirming that the equipment is functioning correctly. Validation protocols are in place to check the accuracy of results before they are reported to the healthcare provider.
The lab follows stringent validation procedures and result interpretation guidelines, ensuring correct reported values. These measures are crucial for maintaining the trustworthiness of lab results, which are essential for diagnosing and managing health conditions.
Challenges and Common Errors in Blood Testing
Blood testing can face challenges despite strict protocols, including issues with analyte stability and pre-analytical errors. Analyte stability refers to the ability of blood components to remain unchanged from collection to analysis. Temperature and time can affect sample quality, making proper handling essential.
Common errors include incorrect sample labeling, mishandling, and improper storage conditions. Laboratories have systems to minimize these errors, including automated error checks and staff training, which help ensure test results are as accurate as possible.
Safety Protocols and Hygiene in Blood Testing
Safety and hygiene are paramount in the blood testing process. Phlebotomists follow strict protocols, including the use of gloves, sterile needles, and alcohol swabs, to protect both themselves and the patients. Adhering to these safety measures minimizes the risk of infection and ensures a safe environment for everyone involved.
Additionally, proper specimen handling protocols are followed to prevent contamination and errors. This includes carefully transporting samples within the lab and ensuring all equipment is properly sanitized. These steps help maintain the integrity of the blood samples and the accuracy of the test results.
Understanding Your Test Results
Once you receive your test results, it’s important to understand what the numbers mean. Results are often presented alongside reference ranges, which indicate the normal values for each test. If your results fall outside these ranges, it may suggest a potential health issue that requires further investigation, highlighting the benefits of early detection through testing.
It is crucial to discuss your results with your healthcare provider, who can interpret them in the context of your overall health and medical history. They can guide you through any necessary lifestyle changes, treatments, or additional tests, helping you take informed steps toward better health.
Conclusion
The General Health Panel Blood Test is essential for monitoring your health and detecting issues early. You gain valuable insights into the process and its importance by understanding the steps involved—from blood draw and sample handling to laboratory analysis and result interpretation. This comprehensive testing approach ensures that your healthcare provider has the information to guide your health decisions effectively.
Regular health checks like the General Health Panel Blood Test are crucial in proactive health management. Knowing what to expect and how to prepare can help you feel more at ease. By staying informed and engaged, you can take charge of your health, address potential issues early, and work towards maintaining a healthier lifestyle.
FAQ’s
What is a General Health Panel Test?
A General Health Panel Test is a comprehensive blood test that assesses overall health by evaluating various body functions, such as liver, kidney, heart, and cholesterol levels. It helps detect potential health issues early, allowing for timely interventions.
How is a Panel Test done?
A panel test involves a trained phlebotomist drawing a blood sample, usually from a vein in your arm. The blood is collected in different tubes, each designated for specific tests. The samples are then processed in a laboratory, where various analyses are conducted to measure key health indicators.
What is a General Health Blood Test?
A General Health Blood Test is part of the General Health Panel that examines various blood components to evaluate overall health. It includes a complete blood count (CBC), lipid panel, liver function tests, and kidney function tests, providing a comprehensive overview of your body’s current state.
What are the five steps for test preparation?
The five key steps for preparing for a General Health Panel Test are:
- Fasting (if required) for 8–12 hours before the test.
- Avoid alcohol and certain medications that can affect test results.
- Staying hydrated makes the blood draw easier.
- Wear loose clothing for easy access to your arm.
- Following specific instructions given by your healthcare provider regarding diet or medication adjustments.
Can I take a General Health Panel Test if I’m on medication?
Yes, you can take the test if you are on medication. Still, it would help if you informed your healthcare provider about your medications or supplements. Some medications can affect test results, and your doctor may provide specific instructions on whether to continue or temporarily stop certain drugs before the test.
How should I prepare for a General Health Panel Test?
Preparation includes fasting 8–12 hours, staying hydrated, avoiding alcohol, and wearing comfortable clothing. To ensure accurate results, it’s important to follow any additional instructions from your healthcare provider, such as avoiding specific foods or medications.
How long does it take to get results from a General Health Panel Test?
Results from a General Health Panel Test typically take 1–3 days, depending on the complexity of the tests and the laboratory’s workload. Your healthcare provider will usually contact you once the results are available, or you can access them through a secure patient portal.