Drug and alcohol test is an essential practice in various fields, including workplaces, legal environments, and medical settings. These tests are designed to detect the presence of substances in the body. They are used to ensure safety, compliance with regulations, and overall well-being. Different testing methods are available, each offering unique benefits and being suited to specific situations. Understanding these methods is crucial for choosing the right test based on Accuracy, detection period, and convenience.
The five most common ways to test for drugs and alcohol are:
- Urine Testing
- Blood Testing
- Saliva (Oral Fluid) Testing
- Hair Follicle Testing
- Breath Testing
Each of these methods has distinct advantages, making them suitable for different scenarios, from workplace safety checks to law enforcement and healthcare settings.
Urine Testing
Urine testing is one of the most widely used methods. It detects a range of drugs and alcohol by analyzing a urine sample for the presence of metabolites—substances produced when the body processes drugs. It’s non-invasive, cost-effective, and suitable for detecting recent drug and alcohol use.
Urine testing is one of the most common methods for detecting drugs and alcohol. The process involves collecting a urine sample, which is then analyzed in a lab to detect the presence of specific substances and their metabolites. Urine tests are non-invasive, relatively easy to administer, and can detect a wide range of drugs.
Urine tests can detect various substances, including marijuana, cocaine, opiates, amphetamines, and alcohol. They are also capable of identifying the metabolites left behind after the body processes these substances, providing a comprehensive picture of recent use.
While urine tests are generally accurate, they could be more foolproof. Factors like hydration levels, the time of consumption, and the test’s sensitivity can affect results. There is also a risk of false positives or negatives, though confirmatory tests can mitigate this.
Common Uses
Urine testing is widely used in workplaces for employee screening, in sports to ensure athletes are clean, and in rehabilitation programs to monitor abstinence.
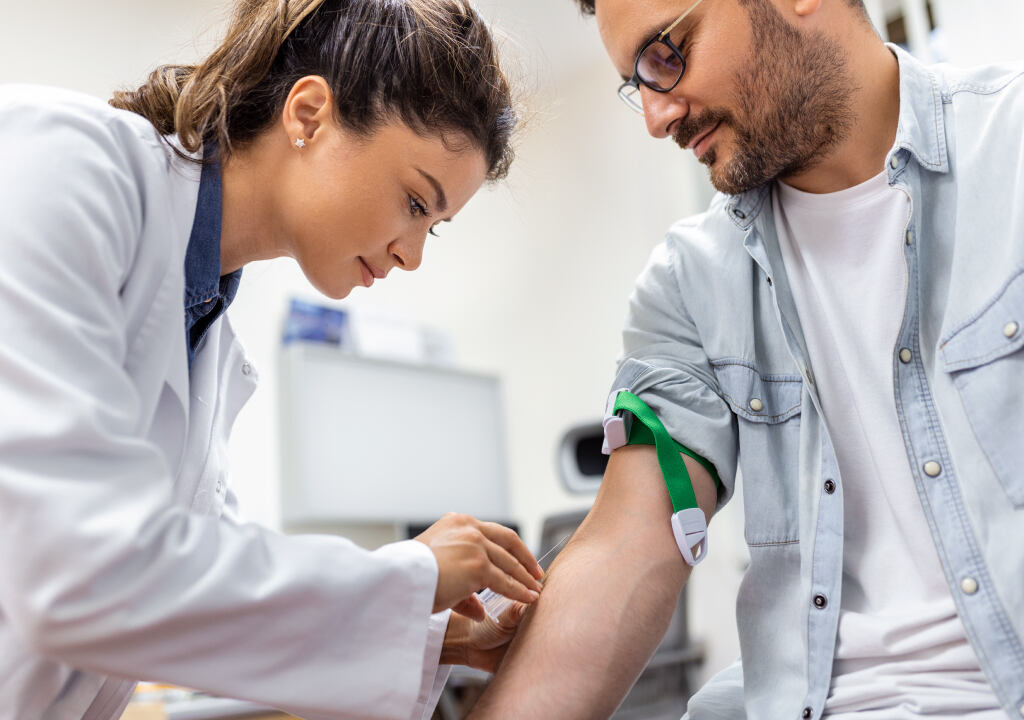
Blood Testing
Blood testing measures the exact concentration of drugs or alcohol in the bloodstream. This method is highly accurate but more invasive than others, typically requiring a blood draw. Blood tests are often used in medical settings and legal situations, such as DUI cases, to determine current intoxication levels.
Blood testing involves drawing a blood sample and analyzing it for the presence of drugs and alcohol. This method is highly accurate and provides a direct measurement of the substance levels in the bloodstream.
Blood tests have a shorter detection window compared to other methods. Drugs and alcohol are usually detectable in blood for a few hours to a few days after use, making this test ideal for identifying recent consumption.
Blood tests can detect a wide range of substances, including alcohol, marijuana, cocaine, opiates, amphetamines, and more. It can also measure the exact amount of alcohol in the bloodstream, known as Blood Alcohol Concentration (BAC).
Common Uses
Blood testing is commonly used in medical settings, during DUI investigations, and for chronic use monitoring where precise levels of substances need to be determined.
Saliva (Oral Fluid) Testing
Saliva testing, also known as oral fluid testing, is a quick and non-invasive method. A swab is used to collect saliva from the mouth, which is then tested for drugs and alcohol. It’s particularly effective for detecting recent use, making it popular in the workplace and roadside testing.
Saliva testing, also known as oral fluid testing, involves collecting saliva from the mouth using a swab. This sample is then tested for the presence of drugs and alcohol. It is a non-invasive, quick, and easy method that can be conducted almost anywhere.
Saliva tests can detect substances such as marijuana, cocaine, amphetamines, opiates, and alcohol. They are effective in detecting substances that have been used within a short period before the test.
Saliva tests have a shorter detection window, typically within 24 to 48 hours of use. It makes them ideal for detecting recent drug or alcohol use.
Common Uses
Saliva testing is often used in workplace drug testing, roadside DUI checks, and situations where immediate results are needed.
Hair Follicle Testing
Hair follicle testing provides a long-term view of drug use, as it can detect substances up to 90 days after consumption. A small hair sample is analyzed for drug molecules deposited in the hair shaft. This method is often used in legal cases and employment screenings to assess long-term substance use.
Hair follicle testing involves taking a small sample of hair, usually from the scalp, and analyzing it for drug use. The hair is examined in a lab to detect drug molecules that are deposited in the hair shaft.
Hair tests have the longest detection window of all testing methods. They can detect drug use for up to 90 days, providing a comprehensive history of substance use.
This method can detect a wide range of drugs, including marijuana, cocaine, opiates, amphetamines, and others. It is not typically used for alcohol detection.
Common Uses
Hair follicle testing is commonly used in legal cases, employment screening, and situations where a long-term history of drug use needs to be assessed.
Breath Testing
Breath testing, commonly associated with breathalyzers, measures blood alcohol concentration (BAC) by analyzing the air exhaled from the lungs. It provides immediate results and is widely used by law enforcement for DUI checks and in workplaces to monitor alcohol consumption.
Breath testing, most commonly associated with the Breathalyzer, measures the amount of alcohol in the breath, which correlates with the Blood Alcohol Concentration (BAC). The individual blows into a device, and the results are provided almost instantly.
Breath tests are specifically used to measure alcohol levels. They provide immediate results, making them ideal for determining current intoxication levels.
Breath tests are generally accurate, but factors such as the calibration of the device, the individual’s metabolism, and even the presence of certain substances in the mouth can affect results.
Common Uses
Breath testing is widely used by law enforcement during DUI checks, in the workplace to ensure employees are not under the influence of alcohol, and in various other settings where immediate alcohol detection is required.
Understanding what is drug and alcohol test helps individuals and employers make informed decisions about which testing method suits their needs, ensuring safety and compliance in various environments.
Comparing Drug and Alcohol Testing Methods
When choosing a testing method, several factors should be considered, including Accuracy, detection window, invasiveness, and cost:
Accuracy and Reliability
Blood tests are considered the most accurate, followed by urine, saliva, hair, and breath tests.
Detection Windows
Hair testing offers the longest detection period (up to 90 days), followed by urine, blood, and saliva tests. Breath tests detect alcohol use at the moment of testing.
Invasiveness and Convenience
Saliva and breath tests are the least invasive and most convenient, while blood and hair tests are more invasive and require lab processing.
Cost Considerations
Urine and saliva tests are generally more affordable. In contrast, blood and hair tests tend to be more expensive due to the complexity of the analysis.
Legal and Ethical Considerations in Drug and Alcohol Testing
Drug and alcohol testing raises several legal and ethical issues:
It’s important to ensure that testing respects individuals’ privacy and that results are kept confidential.
Testing must comply with federal, state, and local laws, including obtaining consent and following proper procedures.
Consent and Awareness
Individuals should be fully informed about the testing process and provide consent before any tests are conducted.
Employers should establish clear, fair policies regarding drug and alcohol testing, including when and how tests will be administered.
The Role of Drug and Alcohol Testing in Public Safety
Drug and alcohol testing plays a critical role in maintaining public safety:
Testing helps prevent impaired driving by identifying drivers under the influence of alcohol or drugs.
Testing ensures that employees are not under the influence while on the job, reducing the risk of accidents and injuries.
Health Monitoring:
In medical settings, testing helps monitor patients for substance abuse, ensuring they receive appropriate care.
Technological Advances in Drug and Alcohol Testing
The field of drug and alcohol testing is constantly evolving, with new technologies improving Accuracy and convenience:
New Testing Methods
Advancements include more accurate and less invasive testing methods, such as instant saliva tests. Enhanced detection techniques are making it harder to tamper with or fool tests.
Remote Testing
At-home and on-site testing technologies are making it easier for individuals to be tested in non-traditional settings.
As technology advances, testing methods will become even more reliable, accessible, and integrated into various aspects of public safety and health monitoring.
Conclusion
Drug and alcohol testing is a critical tool for ensuring safety, compliance, and health across various settings. Understanding the different testing methods and their respective benefits and limitations allows for informed decision-making. Whether for workplace safety, legal compliance, or personal health, choosing the right test can make all the difference in maintaining a drug-free environment.
To fully grasp how does a drug test work, it’s essential to know that tests typically detect substances through samples like urine, blood, hair, or saliva. These tests measure the presence of drugs or their metabolites, offering insights into recent or long-term drug use depending on the method used.
FAQ’s
What is the most common drug and alcohol test?
The most common drug and alcohol test is the urine test. It is widely used in various settings, including workplaces, medical facilities, and legal situations, due to its ease of administration, cost-effectiveness, and ability to detect a wide range of substances.
What is the most common way to test for drugs?
The most common way to test for drugs is through a urine test. Urine testing is popular because it can detect the presence of multiple drugs, including marijuana, cocaine, opiates, and amphetamines, and it provides reliable results for recent drug use.
What is the most common way to test for alcohol?
The most common way to test for alcohol is the breath test. This test uses a breathalyzer to analyze the breath and measure the blood alcohol concentration (BAC). It’s widely used by law enforcement during roadside checks and in workplaces to monitor alcohol consumption.
What are the two tests for alcohol?
The two primary tests for alcohol are:
- Blood Test: Determines the exact amount of alcohol in the bloodstream, offering highly accurate results.
- Breath Test (Breathalyzer): Measures blood alcohol concentration (BAC) from a breath sample.
How many ways can you test for alcohol?
There are four main ways to test for alcohol:
- Breath Test: The most common method using a breathalyzer.
- Blood Test: Measures the precise BAC level in the blood.
- Urine Test: Detects alcohol and its metabolites in the urine, though it’s less precise than breath or blood tests.
- Saliva Test: A less common method, it can detect alcohol in oral fluids for a short period after consumption.